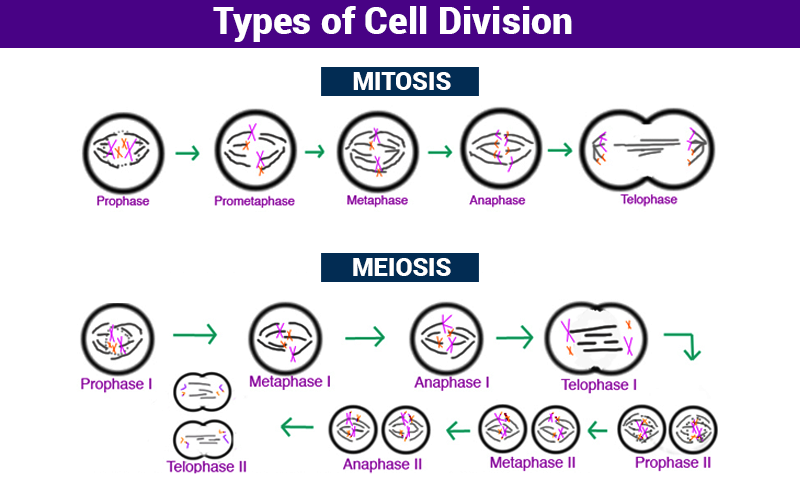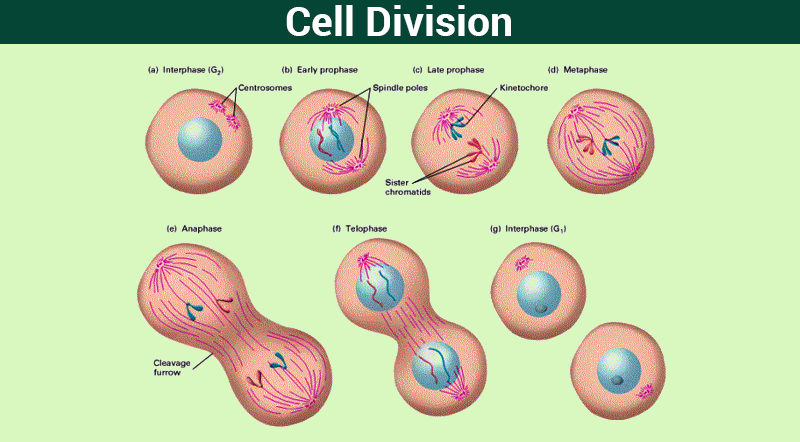
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides, when a mother cell divides into two or more daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle. In eukaryotes, there are two distinct types of cell division; a vegetative division, whereby each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell (mitosis), and a reproductive cell division, whereby the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is reduced by half to produce haploid gametes (meiosis). In cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle, in which, replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei.

Cell division happens when a parent cell divides into two or more cells called daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle. All cells reproduce by splitting into two, where each parental cell gives rise to two daughter cells.